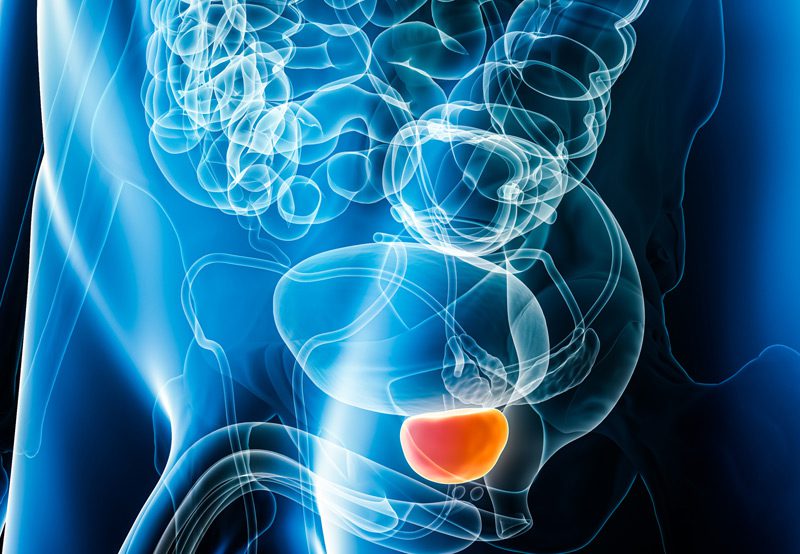
Radical prostatectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove the entire prostate gland and some surrounding tissue, typically as a treatment for localized prostate cancer. The goal of the surgery is to eliminate the cancer while preserving urinary and sexual function whenever possible.
Causes of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer arises from abnormal cell growth in the prostate gland, which is responsible for producing seminal fluid. Key risk factors include:
- Age: Most common in men over 50
- Family History: A genetic predisposition can increase risk
- Race: African American men face a higher risk and more aggressive disease
- Hormonal Influence: Androgens can play a role in tumor growth
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet, obesity, and inflammation may contribute to disease development

Diagnosis
Diagnosis of prostate cancer usually involves:
- PSA Testing: Measures prostate-specific antigen levels in the blood
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): Detects irregularities in prostate shape or size
- Prostate Biopsy: Confirms the presence of cancer and helps determine grade
- MRI or Bone Scan: May be used to assess the extent of disease
Once confirmed, treatment decisions are based on cancer staging, PSA levels, Gleason score, and patient factors.
Treatment Options
Radical prostatectomy is typically offered to patients with localized or locally advanced prostate cancer who are healthy enough for surgery. There are different approaches to the procedure:
- Open Prostatectomy: Traditional method with a larger abdominal incision
- Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: Uses smaller incisions and a camera
- Robotic-Assisted Prostatectomy: Offers enhanced precision, better visualization, and potentially faster recovery
The procedure involves complete removal of the prostate and often the seminal vesicles. Depending on cancer risk and location, nearby lymph nodes may also be removed for evaluation.
Next Steps
Following radical prostatectomy, patients are closely monitored through routine PSA testing to ensure the cancer does not return. Most patients are discharged within one to two days, with full recovery taking several weeks. Side effects such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction can occur, but nerve-sparing techniques and pelvic floor therapy may improve outcomes. Early treatment through radical prostatectomy offers a curative option for many men with prostate cancer, especially when detected at an early stage.
